Glossary Related To Nuclear Medicine
Your go-to resource for understanding essential terms in nuclear medicine. Clear definitions for key concepts in imaging, therapy, and radiopharmaceuticals. Perfect for students and healthcare professionals alike.
- Biopsy
- noun
- A biopsy is a medical procedure involving the removal of a small sample of tissue or cells from the body for examination under a microscope. It is typically performed to diagnose or assess the severity of a suspected disease or abnormality, such as cancer, infection, or inflammation.
- Example: The doctor recommended a biopsy of the suspicious lump in order to determine whether it was cancerous or benign.
- en: Biopsie

- Contrast
- noun
- In the context of medical imaging, contrast refers to the use of substances or techniques that enhance the visibility of structures or abnormalities within the body. These substances, known as contrast agents, are typically administered orally, intravenously, or through other routes before imaging procedures such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Contrast agents work by altering the absorption, transmission, or emission of electromagnetic radiation or magnetic fields, thereby creating clearer distinctions between different tissues or organs. This improved contrast enables healthcare professionals to more accurately diagnose and monitor various medical conditions.
- Example: -The contrast dye injected into the patient's bloodstream helped highlight the blood vessels during the MRI scan.
- en: Contrast

- Cyclotron
- noun
- A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged particles, such as protons or ions, in a spiral path using a combination of magnetic fields and electric fields. This acceleration process allows the particles to reach high energies, which can be used for various applications, including nuclear medicine.
- Example: The hospital installed a cyclotron to produce radioisotopes for medical imaging procedures, such as PET scans, providing a local and reliable source of radiopharmaceuticals for diagnosing and treating patients with cancer and other diseases.
- en: Cyclotron

- Dosimetry
- noun
- Dosimetry is the measurement and calculation of the absorbed dose of radiation received by an individual or a specific area of tissue. It involves the use of specialized instruments and techniques to assess the amount of radiation exposure, ensuring that it remains within safe limits for patients, workers, and the general public.
- Example: Dosimetry plays a crucial role in radiation therapy, where precise measurement and monitoring of the radiation dose delivered to cancerous tumors are essential to ensure effective treatment while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- en: Dosimétrie

- Gamma
- noun
- Gamma radiation, a type of electromagnetic radiation, is highly penetrating and consists of photons emitted from the nucleus of an atom during radioactive decay. It possesses high energy and no mass, enabling it to traverse matter easily. Gamma rays are commonly used in medical imaging, industrial applications, and radiation therapy due to their ability to penetrate deep into materials and tissues while providing valuable diagnostic and therapeutic information.
- Example: -The Earth is bombarded by gamma rays all the time, but usually there aren't enough to do any damage to us. -A burst of gamma rays from space lasting from a fraction of a second to many minutes. -He uses high-resolution solid-state detectors to make precision measurements on the gamma rays emitted
- en: Gamma

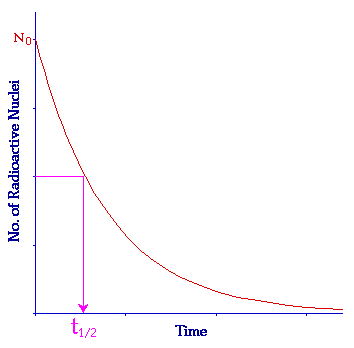
- Half-life
- noun
- Half-life refers to the time it takes for the radioactivity of a substance to decrease to half of its initial value. In the context of nuclear medicine, it is an important parameter used to determine the decay rate of radioactive isotopes.
- Example: The half-life of Technetium-99m is approximately 6 hours, meaning that after 6 hours, only half of the initial amount of Technetium-99m remains radioactive.
- en: Demi-Vie
- Hot Lab
- noun
- A hot lab is a specially designed facility within a nuclear medicine department or radiopharmacy where radioactive materials, such as radiopharmaceuticals, are handled, prepared, and stored. The hot lab is equipped with lead-lined walls, shielding materials, and ventilation systems to ensure the safety of personnel and the surrounding environment. It is called a "hot" lab because it deals with radioactive materials, which are often referred to as "hot." In the hot lab, trained personnel measure, dispense, and quality control radioactive doses for patient administration, as well as handle radioactive waste disposal in accordance with strict regulatory guidelines.
- Example: - The technologist carefully prepared the radiopharmaceutical dose in the hot lab before administering it to the patient for their nuclear medicine scan.
- en: Lab Chaud
- Isotopes
- noun
- Isotopes are variants of a chemical element that have the same number of protons in their atomic nucleus but differ in the number of neutrons. This variation in neutron number results in isotopes having different atomic masses. Isotopes of an element behave similarly chemically but may exhibit different physical properties, such as radioactive decay rates. Isotopes are commonly used in various fields, including nuclear medicine, geology, and environmental science, for purposes such as dating materials, tracing chemical reactions, and medical imaging.
- Example: While each isotope of an element has an identical proton count, the isotopes do not share the same number of neutrons.
- en: Isotopes
- Lead apron
- noun
- A lead apron is a protective garment worn by healthcare personnel during medical imaging procedures, such as X-rays, fluoroscopy, and computed tomography (CT) scans. It is made of a heavy, flexible material containing lead or lead-equivalent material, which effectively absorbs and shields the body from ionizing radiation. Lead aprons are designed to protect the wearer's vital organs, particularly the thyroid, chest, and reproductive organs, from unnecessary radiation exposure. They are an essential safety measure in radiology departments and other medical facilities where radiation-based imaging techniques are used.
- Example: - In the nuclear medicine department, technicians and radiologists frequently wear lead aprons to minimize radiation exposure while performing imaging scans and administering radiopharmaceuticals.
- en: Tablier Plombé

- Lead Shielding
- noun
- Lead shielding refers to the use of lead or lead-based materials to provide protection against ionizing radiation. In nuclear medicine, lead shielding is commonly used to reduce radiation exposure to personnel and the surrounding environment during the handling and storage of radioactive materials, such as radiopharmaceuticals, in facilities like hot labs.
- Example: The nuclear medicine technician wore a lead apron and stood behind lead shielding while preparing doses of radiopharmaceuticals in the hot lab, ensuring minimal radiation exposure during the process.
- en: Protection Plombé

- Oncology
- noun
- Oncology in nuclear medicine refers to the branch of medicine focused on the diagnosis, staging, treatment, and management of cancer using nuclear medicine techniques and technologies. This includes the use of radiopharmaceuticals for imaging tumors, assessing their metabolic activity, and delivering targeted radiation therapy to cancer cells.
- Example: In oncology, nuclear medicine techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) are invaluable for accurately detecting and staging various types of cancer, guiding treatment decisions, and monitoring response to therapy by visualizing metabolic changes within tumors.
- en: Oncologie

- Particle Accelerator
- noun
- A particle accelerator in nuclear medicine is a specialized device used to produce high-energy particles, such as protons or ions, which are utilized for various applications in the field. These accelerators are employed to generate radioisotopes for medical imaging and therapy, including production of radiopharmaceuticals and radioisotopes used in positron emission tomography (PET) and targeted radionuclide therapy.
- Example: The particle accelerator facility was crucial in producing the radioisotopes necessary for the PET scans performed in the nuclear medicine department, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with various medical conditions.
- en: Accelerateur de particule

- Physiology
- noun
- Physiology is the branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their parts, including the processes and mechanisms by which they operate and interact with their environment.
- Example: Studying the physiology of the human cardiovascular system involves examining how the heart pumps blood throughout the body and how blood vessels regulate blood pressure to maintain homeostasis.
- en: Physiologie

- Quality Control
- noun
- Quality control refers to the systematic process of ensuring that products or services meet established quality standards and specifications. It involves monitoring and evaluating various aspects of production or service delivery to detect and correct any deviations or defects that could affect the final outcome. Quality control measures may include inspections, testing, and audits at different stages of the production or service process to maintain consistency, reliability, and customer satisfaction. The goal of quality control is to identify and address issues proactively, ultimately improving the overall quality and reliability of the end product or service.
- Example: - The manufacturing company implemented rigorous quality control measures to inspect and test each product before it is shipped to customers, ensuring that only items meeting the highest standards are delivered.
- en: Control Qualité

- Radiation
- noun
- Energy emitted as particles or waves from a source. It can be natural, like sunlight, or man-made, such as X-rays. Depending on its type, radiation can have different effects on matter and living organisms.
- Example: -Exposure to excessive radiation from the sun can increase the risk of skin cancer.
- en: Radiation
- Radiopharmaceuticals
- noun
- These are specialized drugs that incorporate a small amount of radioactive material. They are administered to patients for diagnostic imaging procedures or therapeutic treatments in nuclear medicine. Radiopharmaceuticals play a vital role in providing valuable diagnostic information and targeted therapy for various medical conditions.
- Example: A new class of cancer drugs called radiopharmaceuticals deliver radiation therapy directly and specifically to cancer cells.
- en: Radiopharmaceutiques

- Radiotherapy
- noun
- Radiotherapy, also known as radiation therapy, is a medical treatment that uses high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells or to alleviate symptoms caused by tumors. It is a common treatment modality for various types of cancer and can be delivered externally (external beam radiotherapy) or internally (brachytherapy).
- Example: After surgery to remove her breast cancer, Sarah underwent a course of radiotherapy to ensure any remaining cancer cells were destroyed, reducing the risk of recurrence.
- en: Radiotherapie

- Scintigraphy
- noun
- Scintigraphy is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses radiopharmaceuticals containing radioactive isotopes to visualize the structure and function of organs and tissues within the body. During a scintigraphy procedure, the radiopharmaceutical is administered to the patient, and its distribution within the body is tracked using a gamma camera. The gamma camera detects the gamma radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceutical as it undergoes radioactive decay, creating images that can reveal abnormalities, such as tumors or areas of inflammation. Scintigraphy is commonly used in nuclear medicine for various purposes, including assessing cardiac function, detecting bone fractures, and evaluating thyroid disorders.
- Example: - The doctor ordered a scintigraphy scan to investigate the function of the patient's thyroid gland using a radioactive tracer injected into their bloodstream.
- en: Scintigraphie
- Theranostics
- noun
- Theranostics is a medical approach that combines diagnostics and therapy into a single integrated process. It involves the use of diagnostic imaging techniques to identify disease characteristics and tailor personalized treatment strategies, often utilizing targeted therapies or radiopharmaceuticals.
- Example: Theranostics revolutionizes cancer treatment by allowing physicians to use molecular imaging to identify tumor-specific markers and then administer targeted therapies, such as radiopharmaceuticals, for precise and effective treatment.
- en: Théranostique
- Tomography
- noun
- Tomography is a medical imaging technique that generates cross-sectional images of the body by combining multiple X-ray or other imaging projections taken from different angles. This process enables visualization of internal structures in detail, allowing for the detection and diagnosis of various medical conditions. Tomography techniques include computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET), each providing unique perspectives and insights into the body's anatomy and function.
- Example: -The doctor ordered a CT scan with tomography to obtain detailed cross-sectional images of the patient's brain, helping to diagnose the cause of their persistent headaches.
- en: Tomographie
